Python 全攻略第一章 Data Types (Part 2)
課程前言
- 接續上週 interger, float, string 等基礎資料型別的介紹,本週主要重點是探討 list (串列), dictionary (字典) 及 tuple (值組,元組?) 三種 data type。
- 謝謝 Chris兄 與 Darren兄 介紹 VSCODE+jupyter notebook 以及 markdown ,筆記是將 jupyter notebook 轉換成 markdown 格式,再進行微調。
- 因 VSCODE 的 GUI 輸出只限於 Python Script, PDF 及 HTML 三種格式,若要輸出為 markdown 格式,請參考這篇,或是 nbconvert 的說明文件。
- 分享一個 VSCODE 套件 MPE (Markdown-preview-enhanced), 以所見即所得的方式同步編修 markdown 格式檔,其說明及安裝方式可參考這裡。
補充材料
- Markdown 學習資源: 教學與線上練習 10 minute tutorial, 下載 MD 單張速查表 cheatsheet。
- Hash table: 還不錯的二篇文章,請參考 雜湊表 Hash Table ,或是 資料結構學習筆記:雜湊表。
- 有關 Tuple 的好文章,可以參考 有了串列 List,為何還要有值組 Tuple 及 使用 Tuple 的好處。
- 有關幾個 Data type,易讀易懂的好文, 敬請參考右邊的連結 → String , List 與 Dictionary。
課程歸納
-
以下這個表格是聽完 Wilson 老師影音課程內容後的綜整結果。
- Primitive Data Type (Basic Type): int, float, str, bool
- Type Casting: int, float, str, list, dic, tuple, set
- Immutable Data Type: int, float, string, bool, tuple
- Mutable Data Type: list, dict, set
| Name | Type | Description | Copy By? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integer | int | Whole numbers, such as -5, 0, 16 | By Value Primitive |
| Float | float | Numbers with decimal point, such as 10.25, 0.04, 3.14159 | By Value Primitive |
| String | str | Ordered sequence of characters, such “Aloha” | By Value Primitive |
| Boolean | bool | Logical value indicating True or False | By Value Primitive |
| List | list | Ordered sequence of data, such as [12, “Hello”, True] * List is just like array in other programming languages * use copy() to make a copy |
By Reference Non-primitive |
| Dictionaries | dict | Unordered key-value pairs, such as {“name”:“Wilson”, ”age”:25} * Dict is just like objects in other programming languages * key: has to be immutable & hashable (int, float, bool, string, tuples) * Sometimes it would be very convenient to use list as a dictionary key for example, {(latitude1, longitude1):location1, (latitude2, longitude2):location2, …} Python uses tuples to solve this problem |
By Reference Non-primitive |
| Tuples | tup | Ordered immutable sequence of objects, such as (10, “100”, ”Hello”) * In short, tuples are just immutable list |
By Reference Non-primitive |
| Sets | set | Unordered collection of unique objects {“a”, “b”} | By Reference Non-primitive |
21 Introduction to Lists
friend1 = "Joe"
friend2 = "Jay"
friend3 = "Joy"
print(f"{friend1}, {friend2}, {friend3} are my friends.")
print("----------------------")
friendList = ["Joe","Jay","Joy"] #採用 list 來存放, 好處是可用 loop 走訪list中的每個元素
print(f"{friendList[0]}, {friendList[1]}, {friendList[2]} are my friends.")
Joe, Jay, Joy are my friends.
----------------------
Joe, Jay, Joy are my friends.
- len(myList), myList[index], myList.count
friendList = ["Joe","Jay","Joy"] #indexing rule and slicing rule work with list
print(f"{friendList[0]}, {friendList[1]}, {friendList[2]} are my friends.")
myList = [] #空的 list
print(len(friendList)) # 3 elements
print(len(myList)) # 0 elements
print(friendList[-1]) #取最後一個值 Joy
print("----------------------")
x = [1, 2, 1]
print(x.count(1)) # 1在 list 中出現的次數 -> 2
Joe, Jay, Joy are my friends.
3
0
Joy
----------------------
2
- slicing[起始index:結束index+1:Step], list concatenate 用加號
#slicing
luckynumbers = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10]
print(luckynumbers[0:3]) #Return list [2, 3, 4]
print(luckynumbers[::2]) #Return index為偶數位置的List [2, 4, 6, 10]
print(luckynumbers[::-1]) #reverse a List
print("----------------------")
x = [1, 2, 1]
y = [3, 4, 5]
print(x + y) #concatenate list by +
print(y * 3) #list 可乘以整數
print("----------------------")
#list is mutable
z = [ 7, 8, 9]
z[1] = 10 # [7, 10, 9]
print(z)
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 4, 6, 10]
[10, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2]
----------------------
[1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 5]
[3, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5]
----------------------
[7, 10, 9]
22 List Functions I
- insert(), reverse()
friends = ["Wilson", "Mike", "Nelson", "Greg", "Jimmy"]
friends.insert(2, "Joe")
print(friends)
print("----------------------")
friends.reverse() #反轉 method 1
print(friends)
print("----------------------")
friends = friends[::-1] #反轉 method 2
print(friends)
['Wilson', 'Mike', 'Joe', 'Nelson', 'Greg', 'Jimmy']
----------------------
['Jimmy', 'Greg', 'Nelson', 'Joe', 'Mike', 'Wilson']
----------------------
['Wilson', 'Mike', 'Joe', 'Nelson', 'Greg', 'Jimmy']
- sort(), remove(), clear()
friends = ["Wilson", "Mike", "Nelson", "Greg", "Jimmy"]
friends.sort() #預設 字串 依字母順序排列
print(friends)
print("----------------------")
numbers=[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, -3]
numbers.sort() #預設 數字 則由小到大排列
print(numbers)
print("----------------------")
friends.remove("Greg")
print(friends)
print("----------------------")
friends.clear()
print(friends)
['Greg', 'Jimmy', 'Mike', 'Nelson', 'Wilson']
----------------------
[-3, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
----------------------
['Jimmy', 'Mike', 'Nelson', 'Wilson']
----------------------
[]
23 List Functions II
- append(), pop()
friends = ["Wilson", "Mike", "Nelson", "Greg", "Jimmy"]
friends.append("John")
friends.append("Sam")
friends.append(15.0) # 不同 data type 亦可 append
print(friends)
['Wilson', 'Mike', 'Nelson', 'Greg', 'Jimmy', 'John', 'Sam', 15.0]
newfriends = ["Wilson", "Mike", "Nelson", "Greg", "Jimmy"]
myPopedFriend = newfriends.pop() #從list中取出最後一個,同時會存下被pop的資料
print(newfriends)
print("----------------------")
print(myPopedFriend)
['Wilson', 'Mike', 'Nelson', 'Greg']
----------------------
Jimmy
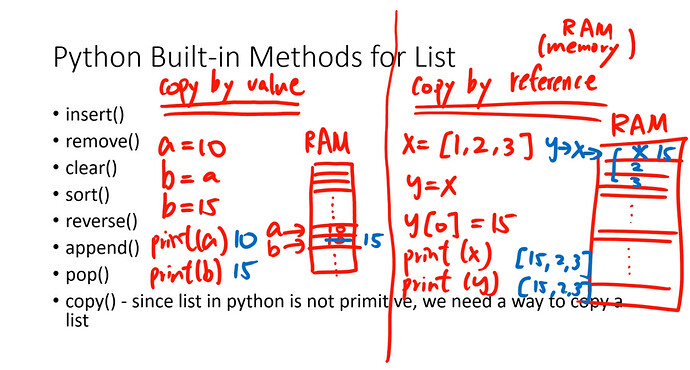
- copy by value & copy by reference
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
y = x # copy by reference
y[0] = 15
print(x) #[15, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print(y) #[15, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print("----------------------")
#因為 list 為 copy by reference 要真正 clone 一個 list,就要採用 copy()
c = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
d = c.copy() # copy by value
d[0] = 15
print(c) #[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print(d) #[15, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[15, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[15, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
----------------------
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[15, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
- list of lists
# list 裡面的 element 中,也含有 list 的取值方式
x = [1, 2, [4, 5, 6], 2, 1, [4, 3, [-10, 4]]]
print(x[2]) # 取得 index為 2 的值 --> 為一整個第二層 list [4, 5, 6]
print("----------------------")
print(x[2][1]) # [][] 取得第二層 list 中,index 為 1 的值 --> 5
print("----------------------")
print(x[5][2][0]) # [][][] 取得第三層 list 中 index 為 0 的值 -->-10
print("----------------------")
y = [1, 2, 3, 4, -2, 5, 7, 8,-4, 10]
print(y[len(y)-1]) # 當list很長時,快速取得最後一個值
[4, 5, 6]
----------------------
5
----------------------
-10
----------------------
10
24 Introduction to dicts
person1 = {"name":"Wilson", "age":25}
print(person1["name"])
print(person1["age"])
print("----------------------")
# what data type can be used for values? Ans: 任何 Data type
person2 = {"x":{"age":[10, 20, 30]}}
print(person2["x"]["age"][0])
print("----------------------")
person3 = {} # 空的 dictionary
person3 ["name"] = "Grace" #塞入 key-value pair 至 dictionary 中
person3 ["age"] = 26 #塞入 key-value pair 至 dictionary 中
print(person3) # {'name': 'Grace', 'age': 26}
print("----------------------")
#dictionary is mutable
person4 = {'name': 'Grace', 'age': 26}
person4 ["name"] = "Joe"
print(person4 )
Wilson
25
----------------------
10
----------------------
{'name': 'Grace', 'age': 26}
----------------------
{'name': 'Joe', 'age': 26}
25 Dictionary Functions
- keys(), values(), items() → item 即是 key-value pair
person5 = {'name': 'Grace', 'age': 26}
print(person5.keys()) #未來可用於 loop
print("----------------------")
print(person5.values())
print("----------------------")
print(person5.items()) # something like a list of tuples
dict_keys(['name', 'age'])
----------------------
dict_values(['Grace', 26])
----------------------
dict_items([('name', 'Grace'), ('age', 26)])
26 Type can be used for keys
- 條件: immutable, hashable
- Integers
- float
- boolean
- string
- 所有元素均為 immutable 的 tuples
27 Introduction to Tuples
- ordered immutable sequence of objects
- 為 immutable list - 能改變 list 的 method 當然都不能用,例如: pop, append, sort, reverse 等等
myTuple = (10, "100", "Hello") # use parenthesis ()
print(len(myTuple)) # 3
print("----------------------")
print(myTuple[0]) # 10 -> indexing 由 index 查 其資料的值
print(myTuple.index("Hello")) # 2 由資料的值 反查 index
print(myTuple[0:2]) # 取得 index 為 0, 1 的元素 -> slicing 適用
myTuple.append(150)
print(myTuple)
3
----------------------
10
2
(10, '100')
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
c:\Users\joe.hu\Desktop\Python Codes\MyNote21-29.ipynb Cell 27 line 9
<a href='vscode-notebook-cell:/c%3A/Users/joe.hu/Desktop/Python%20Codes/MyNote21-29.ipynb#X30sZmlsZQ%3D%3D?line=5'>6</a> print(myTuple.index("Hello")) # 2 由資料的值 反查 index
<a href='vscode-notebook-cell:/c%3A/Users/joe.hu/Desktop/Python%20Codes/MyNote21-29.ipynb#X30sZmlsZQ%3D%3D?line=6'>7</a> print(myTuple[0:2]) # 取得 index 為 0, 1 的元素 -> slicing 適用
----> <a href='vscode-notebook-cell:/c%3A/Users/joe.hu/Desktop/Python%20Codes/MyNote21-29.ipynb#X30sZmlsZQ%3D%3D?line=8'>9</a> myTuple.append(150)
<a href='vscode-notebook-cell:/c%3A/Users/joe.hu/Desktop/Python%20Codes/MyNote21-29.ipynb#X30sZmlsZQ%3D%3D?line=9'>10</a> print(myTuple)
AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'append'
28 Tuple Packing and Unpacking
x = 10, 15 # TUPLE PACKING -> Data separated by comma will be auto-packed into a tuple
y = 11, 12, 15, 16, 19, 23
print(x)
print(y)
print(type(x)) # 查詢屬於何種 data type
print(type(y)) # 查詢屬於何種 data type
print("----------------------")
# Tuple unpacking
z = ("a", "b", "c", "d", "e")
y1, y2, y3, y4, y5 = z # assign a tuple to multiple variables(separated by comma) to unpack it
print(y1)
print(y2)
print(y3)
print(y4)
print(y5)
(10, 15)
(11, 12, 15, 16, 19, 23)
<class 'tuple'>
<class 'tuple'>
----------------------
('a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e')
a
b
c
d
e
29 Mutable objects in tuples
# if an element inside a tuple is mutable, then we can just select it and change it.
myTuple = ([1, 2, 3], "Wilson") # 此 Tuple 內含有 mutable 及 immutable 的 二個 element
myTuple[0][1] = 100 # 即便 tuple 是 immutable,但我們改動的是第一個元素 list(mutable) 內的元素,則可行。,
print(myTuple) # result -> ([1, 100, 3], 'Wilson')
# Q: 那含有 mutable object 的 tuple,還能當做 dictionary 的 key 嗎?
# A: If we want to use a tuple as a dictionary key, then all elements in the tuple have to be immutable.
([1, 100, 3], 'Wilson')
練習: 何者能當做 dict 的 key?
- 15 → Yes
- ‘Bob’ → Yes
- (‘Tom’, [14, 23, 27]) → No: 第二個元素為 mutable 的 list
- [‘filename’, (15, 16)] → No: list 是 mutable,不能當 Key,連 element 都不用檢查
- “filename” → Yes
- (“filename”, 25, “extension”) → Yes
匯出 Jupyter notebook → md
!jupyter nbconvert --to markdown Mynote21-29.ipynb # Thank you, Darren.
[NbConvertApp] Converting notebook Mynote21-29.ipynb to markdown
[NbConvertApp] Writing 10875 bytes to Mynote21-29.md